Squint Surgery Expert in Perumbakkam
Your Trusted Partner in Cataract Surgery
Clinicians perform squint surgery to correct misaligned eyes, enhancing visual alignment and depth perception. Our commitment extends to providing comprehensive care and support throughout the squint surgery process, ensuring optimal outcomes and improved visual function for our patients.
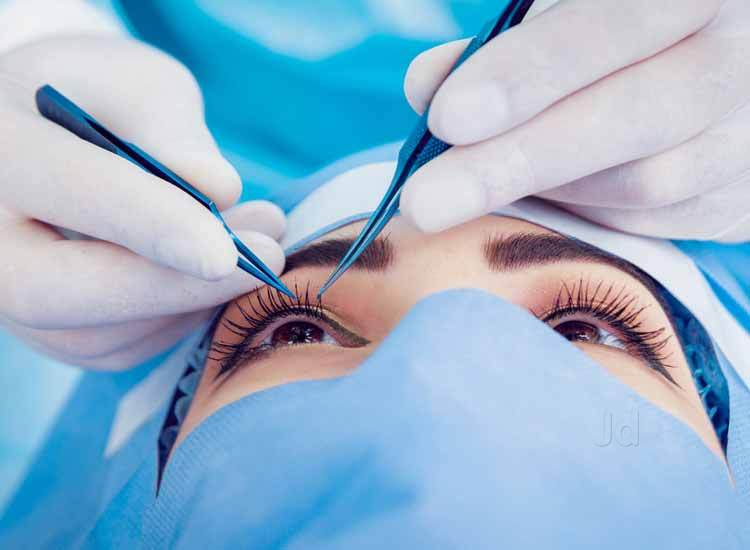
Understanding Squint Surgery
What is Squint Surgery?
Squint surgery, also known as strabismus surgery, is a surgical procedure performed to correct misalignment of the eyes, known as strabismus. During the surgery, the eye muscles responsible for controlling eye movement and alignment are adjusted to realign the eyes and improve their coordination. Squint surgery aims to restore binocular vision, enhance depth perception, and improve the cosmetic appearance of the eyes. It is typically performed on an outpatient basis under general anesthesia or sedation, and the specific surgical technique may vary depending on the type and severity of strabismus.
What are Squint Surgery Types?
Squint surgery, or strabismus surgery, encompasses various techniques depending on the type and severity of the misalignment. Common types of squint surgery include:
Recession: In recession surgery, one or more of the eye muscles are weakened by moving their insertion farther back on the eyeball, reducing the muscle’s pull and allowing the eye to align properly.
Resection: Resection surgery involves shortening one or more of the eye muscles by removing a portion of the muscle, increasing its tension and pulling power to correct misalignment.
Adjustable Suture Surgery: This technique involves placing temporary sutures during surgery, which can be adjusted postoperatively to fine-tune eye alignment while the patient is awake and cooperative.
Transposition: Transposition surgery involves repositioning one or more eye muscles to change their pull direction, typically used for complex cases or when traditional approaches are insufficient.
Oblique Muscle Surgery: This type of surgery targets the oblique muscles of the eye, which control vertical eye movements, and may be performed to correct specific types of strabismus.
What happens before this procedure?
Before squint surgery, several preparatory steps are taken to ensure optimal outcomes. Initially, the patient undergoes a comprehensive eye examination to assess the type and severity of the strabismus, as well as to evaluate overall eye health. This examination may include visual acuity tests, assessment of eye movements, and measurement of the angle of deviation. Additionally, the patient’s medical history is reviewed, including any previous eye surgeries or treatments. If surgery is deemed appropriate, the surgeon discusses the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes with the patient and addresses any questions or concerns. Preoperative instructions, such as fasting before surgery and discontinuation of certain medications, may be provided, and arrangements for anesthesia and postoperative care are made. By completing these preparatory steps, patients can feel confident and well-prepared for their squint surgery, ensuring a smoother treatment experience and better postoperative results.
What happens during these surgeries?
During squint surgery, the following steps typically occur:
Anesthesia: The patient is placed under general anesthesia or sedation to ensure comfort and immobility during the procedure.
Incision: The surgeon makes small incisions in the tissue covering the eye (conjunctiva) to access the eye muscles that need adjustment.
Muscle Adjustment: Using specialized surgical instruments, the surgeon adjusts the tension of the eye muscles by either weakening (recession) or strengthening (resection) them, depending on the type and direction of misalignment.
Suture Placement: Sutures are used to secure the adjusted muscles in their new positions. In some cases, adjustable sutures may be used, allowing for fine-tuning of muscle alignment after surgery.
Closure: The incisions in the conjunctiva are closed with dissolvable sutures, which typically do not require removal.
Postoperative Care: After surgery, the patient is monitored closely for any immediate complications, such as excessive bleeding or infection. Antibiotic ointment may be applied to the eyes, and the patient is given instructions for postoperative care, including eye hygiene, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
What happens after Squint Surgery?
After squint surgery, patients typically experience some discomfort, redness, and swelling around the eyes, which usually subside within a few days. Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. It’s essential for patients to follow postoperative care instructions provided by their surgeon, which may include avoiding rubbing or touching the eyes, using prescribed medications as directed, and attending follow-up appointments for monitoring healing progress and adjusting any necessary postoperative adjustments. While vision may be temporarily blurry or double immediately after surgery, it typically improves as the eyes heal and the muscles adjust to their new positions. Overall, with proper care and follow-up, most patients can expect a successful outcome with improved eye alignment and visual function after squint surgery.
What are the risks or complications of Squint Surgery?
Squint surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries some risks and potential complications, although they are relatively rare. These may include:
Undercorrection or Overcorrection: In some cases, the eyes may not align perfectly after surgery, resulting in residual misalignment (undercorrection) or overcorrection of the squint.
Double Vision: Temporary or permanent double vision (diplopia) may occur after squint surgery, particularly if the eyes are not perfectly aligned or if there is a significant difference in visual acuity between the eyes.
Infection: Although uncommon, there is a risk of postoperative infection (endophthalmitis) at the surgical site, which can lead to severe vision loss if not promptly treated with antibiotics.
Scarring: Excessive scarring of the conjunctiva or surrounding tissues may occur, affecting eye movement and alignment.
Over- or Under-Weakening of Muscles: If the eye muscles are over- or under-weakened during surgery, it may result in inadequate correction of the squint or an imbalance in eye alignment.
Loss of Vision: While rare, there is a small risk of vision loss associated with squint surgery, particularly if there is damage to the optic nerve or other critical structures during the procedure.
Persistent Misalignment: In some cases, the squint may recur or persist despite surgical intervention, requiring additional procedures or treatments to achieve optimal alignment.
Dry Eye Syndrome: Temporary or chronic dry eye symptoms may occur after squint surgery, particularly if the tear film is disrupted during the procedure or if there is inadequate tear production.
Is Squint Surgery worth it?
Whether squint surgery, also known as strabismus surgery, is worth it depends on individual circumstances, including the severity of the squint, its impact on visual function and quality of life, and the potential risks and benefits of the procedure. For many individuals with significant eye misalignment, squint surgery can be a highly effective treatment option, improving eye alignment, enhancing depth perception, and restoring confidence in appearance. While squint surgery carries some risks and requires a period of recovery, the potential benefits of improved eye alignment and visual function often outweigh the risks for those who experience significant social, functional, or psychological impacts due to their squint. It’s important for individuals considering squint surgery to discuss their concerns and goals with an experienced eye surgeon and to make an informed decision based on their unique needs and circumstances.
How long does it take to recover from Squint Surgery?
The recovery time after squint surgery varies depending on factors such as the specific surgical technique used, the extent of the procedure, and individual healing factors. In general, patients can expect some discomfort, redness, and swelling around the eyes immediately after surgery, which typically subside within a few days to a week. Antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to aid in healing and reduce inflammation. While vision may be temporarily blurry or double immediately after surgery, it usually improves as the eyes heal and adjust to their new positions. Most patients can resume normal activities, including school or work, within a few days to a week after surgery, although strenuous activities may need to be avoided for a few weeks. Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing progress and ensure optimal outcomes. Overall, with proper care and follow-up, most patients can expect a successful recovery and improved eye alignment after squint surgery.
Frequently Asked Question on Squint Surgery
Squint surgery, also known as strabismus surgery, is a procedure performed to correct misalignment of the eyes, known as strabismus, to improve eye alignment and visual function.
Candidates for squint surgery typically include individuals with significant eye misalignment that affects visual function, depth perception, or cosmetic appearance.
Squint surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia or sedation, so patients do not feel pain during the procedure. Some discomfort and soreness around the eyes may occur after surgery, but this is usually manageable with pain medication.
In some cases, additional surgeries or treatments may be needed to achieve optimal eye alignment, particularly if the squint is complex or if further adjustments are required.
While squint surgery primarily aims to improve eye alignment and cosmetic appearance, it may also enhance depth perception and visual function in some cases.
During the recovery period, patients may experience some discomfort, redness, and swelling around the eyes, which usually subside within a few days. Follow-up appointments with the surgeon are essential to monitor healing progress and ensure optimal outcomes.
