Kidney Stones Expert In Perumbakkam
Your Trusted Partner in Kidney Stones Treatment
The journey of a kidney stone patient begins with consultation with a Urologist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan. If needed, the urologist may collaborate with other medical experts to provide comprehensive care and guidance.
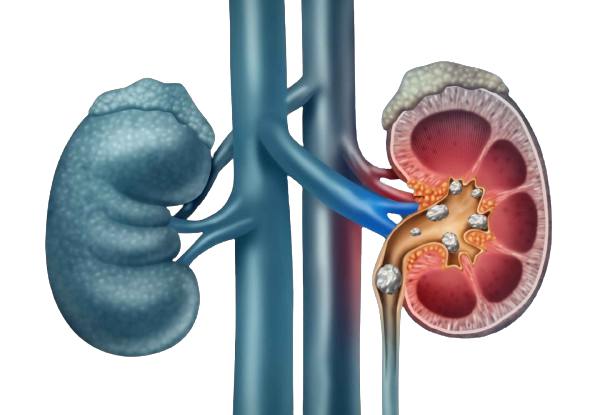
Understanding Kidney Stones
Signs of Kidney Stones
You might be at risk for Kidney Stones if you are experiencing any of the following signs:
- Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen
- Painful urination
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urination
- Urinary urgency
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if an infection is present)
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Difficulty passing urine
Symptoms
- Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen
- Painful urination
- Blood in the urine
- Frequent urination
- Urinary urgency
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills (if an infection is present)
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Weakness or Fatigue
- Difficulty passing urine
- Urinating small amounts or in dribbles
Kidney Stones Treatment in India
NewGen Hospital takes pride in offering a diverse array of treatment programs meticulously tailored to meet the unique needs of individuals facing Kidney Stones. Our dedicated team of professionals crafts personalized treatment plans that consider each patient’s specific circumstances.
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are hard deposits that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. While kidney stones can affect individuals of all ages, they are more commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 30 and 60.
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. When certain substances in the urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become highly concentrated, they can crystallize and form stones.
We are here to provide you with top-notch care and guidance to manage kidney stones effectively.
Risk Factors
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can lead to the formation of concentrated urine, increasing the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Diet: High intake of certain foods, such as salt, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods (e.g., spinach, nuts), can contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
- Family history: Individuals with a family history of kidney stones are at higher risk of developing them.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease, can increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Medications: Some medications, including diuretics and calcium-based antacids, can increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
Prevention
To decrease the likelihood of kidney stones:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain adequate urine volume and prevent the formation of concentrated urine.
- Follow a balanced diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and limit intake of salt, animal protein, and oxalate-rich foods.
- Monitor calcium intake: Consume calcium-rich foods in moderation and avoid excessive calcium supplementation.
- Limit sodium intake: Reduce consumption of high-sodium foods and avoid adding extra salt to meals.
- Manage underlying medical conditions: Work with your healthcare provider to manage conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease that may increase the risk of kidney stones.
Aftercare Services
Aftercare is typically an extension of the main rehabilitation programs that’s aimed at supporting rehabilitation graduates to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Some people find it challenging to maintain normal functions , which is why it’s important that you enrol in an aftercare program.
Recovery is a life-long journey, and aftercare/ alumni programs are there to help you avoid the risk of relapsing. Most aftercare programs are a combination of regular checkups and rehabilitation.
Frequently Asked Questions on Kidney Stones
Common symptoms include severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen, painful urination, blood in the urine, frequent urination, urinary urgency, nausea and vomiting, fever and chills (if an infection is present), cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and difficulty passing urine.
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as imaging studies, urinalysis, blood tests, and 24-hour urine collection.
Treatment may include pain management, fluid intake, medications, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), ureteroscopy, percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), or surgery, depending on the size, location, and composition of the stones.
Prognosis varies based on factors such as the size and composition of the stones, treatment approach, and patient’s overall health. Most kidney stones can be treated successfully, but recurrence is common without preventive measures.
Patients can access various supportive services, including pain management, nutritional support, counselling, and education on preventive measures for kidney stone recurrence.
Clinical trials may be available for individuals interested in participating in research studies aimed at improving the understanding and treatment of kidney stones. Participation in these trials may provide eligible patients with access to innovative treatments and contribute to advancements in the field of urology.
The department offers resources like support groups, educational materials, and referrals to other healthcare professionals to address comprehensive needs throughout the cancer journey.
