Orthopedic Conditions Expert in Perumbakkam
Your Trusted Partner in Orthopedic Conditions
Pediatric orthopedic conditions involve issues with a child’s bones, joints, or muscles, which can affect their growth and mobility. We are here to provide you with exceptional care and expert guidance to address these conditions, ensuring your child’s optimal development and well-being.

Understanding Orthopedic Conditions
What are Orthopedic Conditions?
Pediatric orthopedic conditions are medical issues related to the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments in children. These conditions can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired and can affect growth, movement, and overall physical development. Common pediatric orthopedic conditions include fractures, developmental dysplasia of the hip, clubfoot, scoliosis, and limb length discrepancies. Effective management and treatment are essential for ensuring proper growth and function, and often involve a combination of medical intervention, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery. Here are the common pediatric orthopedic conditions in small points:
- Fractures: Broken bones requiring proper alignment and healing management.
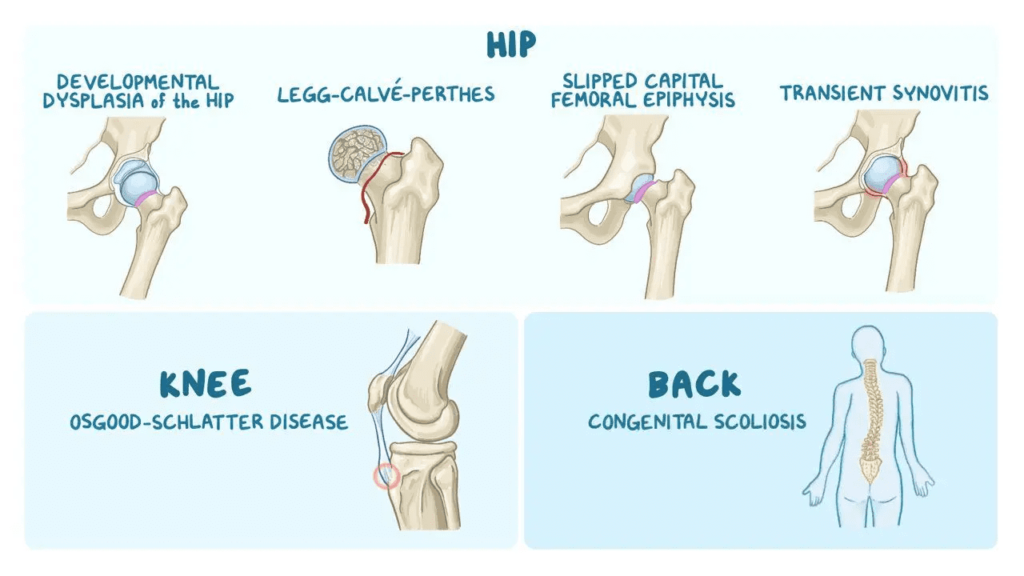
- Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH): Improperly formed hip joint causing instability.
- Clubfoot: Twisted foot shape at birth, treated with stretching, casting, or surgery.
- Scoliosis: Abnormal spine curvature, treated with bracing or surgery.
- Limb Length Discrepancies: Unequal limb lengths, managed with therapy, orthotics, or surgery.
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease: Knee pain and swelling during growth spurts, treated with rest and therapy.
- Cerebral Palsy: Movement and muscle tone disorders from brain damage, managed with therapy and medications.
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA): Joint inflammation and pain in children, treated with medications and therapy.
- Flatfoot: Low or absent foot arch, managed with orthotics or surgery if symptomatic.
- Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease: Hip joint blood supply disruption, treated to maintain hip shape and function.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE): Thigh bone slippage requiring surgical intervention.
- Rickets: Vitamin D deficiency leading to weak bones, treated with supplements and sometimes surgery.
Causes of Orthopedic Conditions
- Genetic Factors: Inherited traits or genetic mutations affecting bone and joint development (e.g., osteogenesis imperfecta).
- Congenital Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities present at birth, such as clubfoot or hip dysplasia.
- Injuries and Trauma: Falls, accidents, or sports injuries leading to fractures or joint damage.
- Infections: Infections like septic arthritis or osteomyelitis causing inflammation and damage to bones or joints.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients, such as vitamin D or calcium, leading to conditions like rickets.
- Overuse and Repetitive Stress: Repeated stress on bones and joints from activities or sports causing conditions like Osgood-Schlatter disease.
- Growth Plate Issues: Problems with the growth plates in children leading to conditions like slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE).
- Neuromuscular Disorders: Conditions like cerebral palsy affecting muscle tone and coordination, leading to orthopedic issues.
- Metabolic Disorders: Disorders affecting bone metabolism, such as hypothyroidism or rickets.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Autoimmune diseases causing joint inflammation, such as juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA).
Reducing pediatric orthopedic conditions involves a combination of preventive measures, early intervention, and education. Ensuring children receive adequate nutrition, including essential vitamins and minerals like calcium and vitamin D, supports healthy bone development. Encouraging safe physical activities and proper sports techniques can help prevent injuries, while regular check-ups allow for early detection and treatment of any developing issues. Educating parents and caregivers about the importance of proper footwear, safe play environments, and recognizing early signs of orthopedic problems is crucial. Additionally, timely medical intervention for congenital conditions and maintaining overall physical health can significantly reduce the incidence and impact of pediatric orthopedic conditions.
Treatments
- Casting and Splinting: Immobilizing broken bones for proper healing.
- Bracing: Supporting and correcting bone and joint alignment.
- Physical Therapy: Improving strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Medications: Managing pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: Correcting severe deformities or repairing damaged tissues.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom supports for improved function and comfort.
- Nutritional Supplements: Ensuring adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
- Activity Modification: Adjusting physical activities to prevent further injury.
- Growth Monitoring: Regular check-ups to monitor development and address issues early.
- Rehabilitation Programs: Comprehensive recovery plans tailored to individual needs.
Frequently Asked Questions on Orthopedic Conditions
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, imaging studies (e.g., X-rays, MRIs), and sometimes blood tests to assess overall health and identify specific conditions.
Prevention includes ensuring proper technique, using appropriate safety gear, encouraging warm-ups and stretching, and avoiding overuse by diversifying activities.
Seek immediate medical attention, as infections like septic arthritis or osteomyelitis require prompt treatment with antibiotics and sometimes surgical drainage.
Physical therapy helps improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion, and is crucial for rehabilitation after injuries or surgeries.
